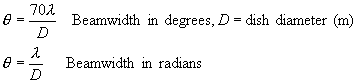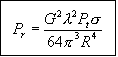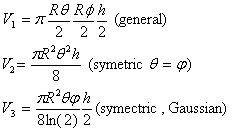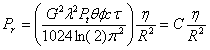| Term | Details |
|---|---|
| Dead Zone |
|
| Range Resolution |
|
| PRF |
Pulse Repetition Frequency |
| PRI |
Pulse Repetition Interval = 1/PRF |
| Unambiguous range |
|
| Doppler shift |
|
| Unambiguous velocity |
|
| Doppler dilemma |
|
| Definition of radar reflectivity h (m2 m-3 ) |
|
| Radar reflectivity h (m2 m-3 ) |
|
| Definition of radar reflectivity factor z (mm6/mm3) |
|
| Radar equation with incorporating simplified "lobing" |
|
| Radar equation with incorporating simplified "lobing" in region below first peak |
|
| Definition of refractivity |
|
| Distance to horizon (linear model of refractivity) |
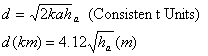
|
| where a = diameter of earth, ha is the antenna height and k = 4/3 | |
| Speed of radio wave |
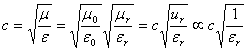 |