55:148 Digital Image Processing
55:247 Image Analysis and Understanding
Chapter 13,
Texture: Syntactic texture description
Chapter 13.2 Overview:
Shape chain grammars
Graph grammars
Primitive grouping in hierarchical textures
- Syntactic texture description approaches are not used as widely as statistical ones.
- Syntactic texture recognition - analogy between texture spatial relationships and structure of a formal language.
- Textures from one class form a language represented by its grammar.
- Recognition process is a syntactic analysis of the texture description word.
- Purely syntactic texture description models are based on idea of almost regular spatial organization of texture primitives.
- Grammar representation - primitives are terminal symbols, relationships are represented as transformation rules.
- Grammar is a very strict formula but real-world textures are frequently irregular - this causes problems.
- Grammar description of textures used more often for texture synthesis.
- Syntactic texture description in reality requires variable rules, and use of non-deterministic grammars.
Shape chain grammars
chain grammars are the simplest grammars usable for texture description
start symbol --> shape rules

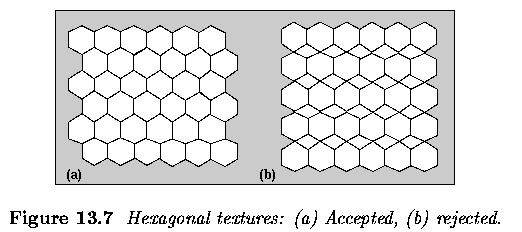
- Example of hexagonal texture generation:

- Texture analysis ...
- texture a) will be accepted as generated by the above grammar
- texture b) will be rejected
Graph grammars
- description using planar graphs
Primitive grouping in hierarchical textures
- Several levels of primitives can be detected in hierarchical textures
- lower level primitives may form a specific pattern which can be considered a primitive at a higher description level

- Primitive grouping detects the hierarchically higher level units in the texture
- Several levels of hierarchies may occur so grouping has to continue until no more grouping is possible

- Grouping plays the same role as feature description in statistical methods - different primitives and/or different spatial relationships represent different textures
- In the figure above, textures can be distinguished as consisting of different primitives after the grouping step



Last Modified: June 8, 1999
![[Go Back]](../IMAGES/next.gif)








