Topic 2 Lesson 2
Units and dimensions, systems of units, dimensional homogeneity
Dimensional Homogeneity
An equation is said to be dimensionally homogeneous if all additive terms
on both sides of the equation have the same dimensions.
To illustrate the idea, lets consider the expression relating two pressures
in a differential manometer:
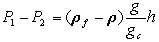
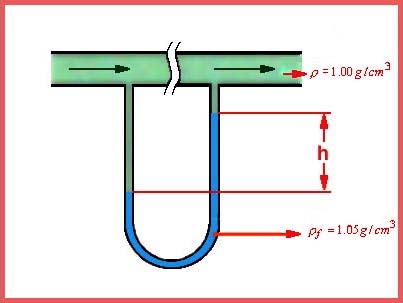
Differential Manometer Equation
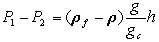
P1 is the pressure exerted on one side of the manometer
(dimension of force/area);
P2 is the pressure exerted on the other side (dimension
of force/area);
 is
the density of the manometer fluid (dimension of mass/volume); is
the density of the manometer fluid (dimension of mass/volume);
 is
the density of the fluid flowing in the pipe (dimension of mass/volume); is
the density of the fluid flowing in the pipe (dimension of mass/volume);
h is the height of the manometer fluid on the low pressure side of
the instrument relative to the height on the high pressure side (dimension
of length)

We will multiply the equation out, then will examine the dimensions
of each term:
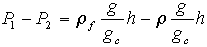
The two terms on the left side of the equation obviously have dimensions
of force/area, therefore, the equation is dimensionally homogeneous
if the quantity ( ·h·g/gc)
also has these units. ·h·g/gc)
also has these units.
 has
dimensions of mass/volume (or mass/length3) has
dimensions of mass/volume (or mass/length3)
h has dimensions of length.
Therefore,  x h has dimensions of mass/length2, or mass/area
x h has dimensions of mass/length2, or mass/area
g has dimensions of length/time2
gc has dimensions of (mass length/time2) / force
Therefore, g/gc has dimensions of force/mass
Therefore, ( h g/gc) has dimensions of force/area, and the equation is
dimensionally homogeneous.
h g/gc) has dimensions of force/area, and the equation is
dimensionally homogeneous.
Dimensional Homogeneity
An equation that is not dimensionally homogeneous cannot possibly be
valid (in fact, it makes no sense).
An equation can be both dimensionally homogeneous and invalid if faulty
reasoning is used to derive the equation.
An equation that is dimensionally homogeneous, but inconsistent in
units, may be made consistent by multiplying by appropriate conversion
factors.
|