55:148 Digital Image Processing
55:247 Image Analysis and Understanding
Chapter 9,
3D Vision (Part I): Geometry for 3D vision
Chapter 9.2 Overview:
Basics of projective geometry
- How to use 2D image information for automated measurement of the 3D
world.
- Perspective projection (central projection) describes image formation
by a pinhole camera or a thin lens.
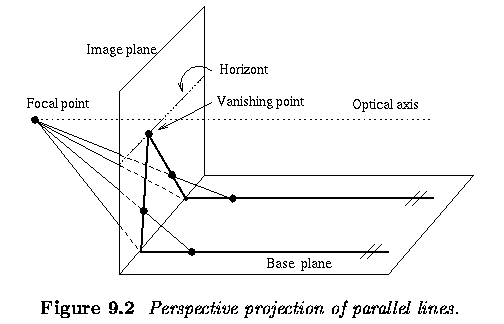
- Basic notation and the definitions.
- Consider (n+1) dimensional space Rn+1 not containing its
origin
- Then equivalence relations can be defined
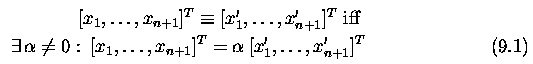
- P is the projective space.
- Points in the projective space are expressed in homogeneous (also projective)
co-ordinates, which we will denote in bold with a tilde.
- Such points are often shown with the number one on the rightmost position,
[x'_1, ..., x'_n, 1]^T.
- This point is equivalent to any point that differs only by nonzero
scaling.
- We are more accustomed to $n$-dimensional Euclidean space R^n.
- The one-to-one mapping from R^n into P^n is given by
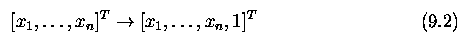
- Only the points x_1, ..., x_n, 0]^T do not have an Euclidean counterpart.
- It is easy to demonstrate that they represent points at infinity in
a particular direction.
- Consider x_1, ..., x_n, 0]^T as a limiting case of [x_1, ..., x_n,
alpha]^T that is projectively equivalent to [x_{1}/alpha, ..., x_{n}/alpha,
1]^T, and assume that alpha --> 0.
- This corresponds to a point in R^n going to infinity in the direction
of the radius vector [x_{1}/alpha,..., x_{n}/alpha]
- A colineation, or projective transformation, is any mapping
P^n -> P^n that is defined by a regular (n+1)x(n+1) matrix A ... ~y
= A ~x.
- Note that the matrix A is defined up to a scale factor.
- Colineations map hyperplanes to hyperplanes; a special case is the
mapping of lines to lines that is often used in computer vision.
The single perspective camera
- Consider the case of one camera with a thin lens (simplest approximation).
- The pinhole camera performs perspective projection.
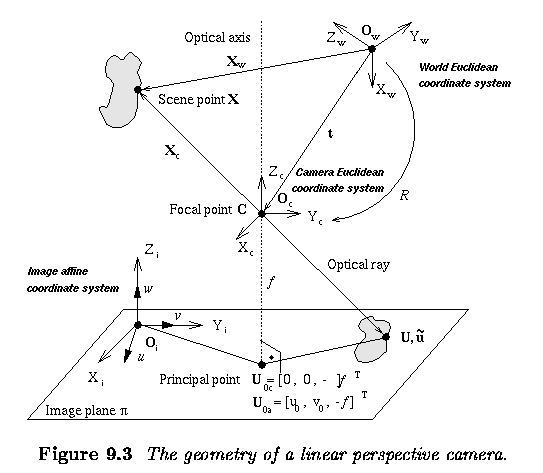
- The geometry of the device is depicted in Figure above; the plane on
the bottom is an image plane pi to which the real world projects,
and the vertical dotted line is the optical axis.
- The lens is positioned perpendicularly to the optical axis at the focal
point C (also called the optical center).
- The focal length f (sometimes called the principal axis distance)
is a parameter of the lens.
- The projection is performed by an optical ray (also a light beam) reflected
from a scene point X.
- The optical ray passes through the optical center C and hits the image
plane at the point U.
- Let's define four co-ordinate systems:
- The world Euclidean co-ordinate system (subscript _w) has origin
at the point O_w.
- Points X, U are expressed in the world co-ordinate system.
- The camera Euclidean co-ordinate system (subscript _c) has the
focal point C = O_c as its origin.
- The co-ordinate axis Z_c is aligned with the optical axis and points
away from the image plane.
- There is a unique relation between world and camera co-ordinate systems.
- We can align the world to camera co-ordinates by performing an Euclidean
transformation consisting of a translation t and a rotation R.
- The image Euclidean co-ordinate system (subscript _i) has axes
aligned with the camera co-ordinate system, with X_i, Y_i lying in the
image plane.
- The image affine co-ordinate system (subscript _a) has co-ordinate
axes u, v, w, and origin O_i coincident with the origin of the image Euclidean
co-ordinate system.
- The axes w, v are aligned with the axes Z_i, X_i, but the axis u may
have a different orientation to the axis Y_i.
- The reason for introducing the camera affine co-ordinates is the fact
that in general, pixels need not be perpendicular and axes can be scaled
differently.
- A camera performs a linear transformation from the 3D projective space
P^3 to the 2D projective space P^2.
- A scene point X is expressed in the world Euclidean co-ordinate system
as a 3x1 vector.
- To express the same point in the camera Euclidean co-ordinate system,
i.e. X_c, we have to rotate it as specified by the matrix R and translate
it by subtracting vector t.
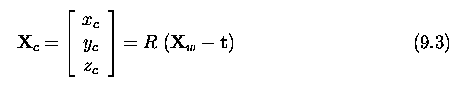
- The point X_c is projected to the image plane pi as point U_c.
- The x and y co-ordinates of the projected point can be derived from
the similar triangles illustrated in Figure 9.4.
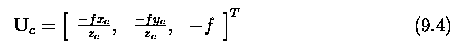
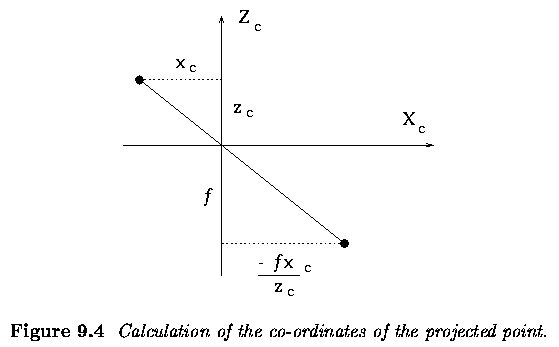
- It remains to derive where the projected point U_c is positioned
in the image affine co-ordinate system, i.e. to determine the co-ordinates
which the real camera actually delivers.
- The image affine co-ordinate system, with origin at the top left corner
of the image, represents a shear and rescaling (often called the aspect
ratio) of the image Euclidean co-ordinate system.
- The principal point U_0 -- sometimes called the center of the image
in camera calibration procedures is the intersection of the optical axis
with the image plane pi.
- The principal point U_0 is expressed in the image affine co-ordinate
system as U_0a=[u_0,v_0,0]^T.
- The projected point can be represented in the 2D image plane pi in
homogeneous co-ordinates as ~u = [U,V,W]^T, and its 2D Euclidean counterpart
is u = [u,v]^T = [U/W,V/W]^T.
- Homogeneous co-ordinates allow us to express the affine transformation
as a multiplication by a single 3x3 matrix where unknowns a, b, c describe
the shear together with scaling along co-ordinate axes, and u_0 and v_0
give the affine co-ordinates of the principal point in the image.
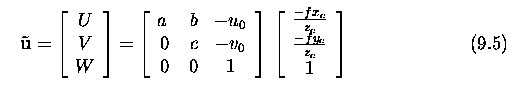
- We aim to collect all constants in this matrix, sometimes called the
camera calibration matrix K.
- Since homogeneous co-ordinates are in use, the equation can be multiplied
by any nonzero constant; thus we multiply by z_c to remove this parameter.
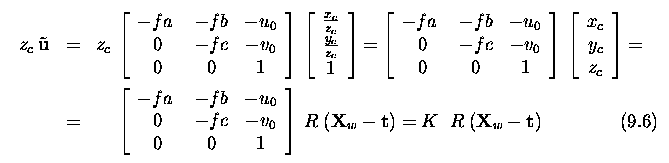
- The extrinsic parameters of the camera depend on the orientation
of the camera Euclidean co-ordinates with respect to the world Euclidean
co-ordinate system (see Figure 9.3).
- This relation is given in equation (9.6) by matrices R and t.
- The rotation matrix R expresses three elementary rotations of the co-ordinate
axes -- rotations along the axes x, y, and z are termed pan,
tilt, and roll, respectively.
- The translation vector t gives three elements of the translation of
the origin of the world co-ordinate system with respect to the camera co-ordinate
system.
- Thus there are six extrinsic camera parameters; three rotations
and three translations.
- The camera calibration matrix K is upper triangular as can be seen
from equation (9.6). The coefficients of this matrix are called intrinsic
parameters of the camera, and describe the specific camera independent
on its position and orientation in space.
- If the intrinsic parameters are known, a metric measurement can
be performed from images.
- Assume momentarily the simple case in which the world co-ordinates
coincide with the camera co-ordinates, meaning that X_w = X_c.
- Then equation (9.6) simplifies to
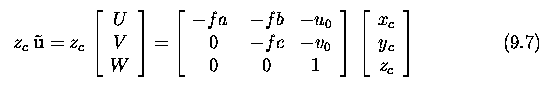
- Two separate equations for u and v
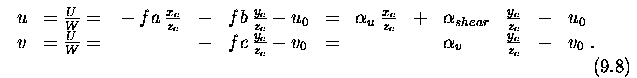
where we make the substitutions alpha_u = -fa, alpha_shear =
-fb, and alpha_v = -fc.
- Thus we have five intrinsic parameters, all given in pixels.
- The formulae also give the interpretation of the intrinsic parameters:
- alpha_u represents scaling in the u axis, measuring F in pixels along
the u axis,
- alpha_v similarly specifies f in pixels along the v-axis.
- alpha_shear measures in pixels in the v-axis direction how much is
the focal length f coincident with u-axis slanted from the Y_i-axis.
- This completes the description of the extrinsic and intrinsic camera
parameters.
- Returning to the general case given by the equation (9.6) ...if we
express the scene point in homogeneous co-ordinates ~X_w = [X_w,1]^T, we
can write the perspective projection using a single 3x4 matrix.
- The leftmost 3x3 submatrix describes a rotation and the rightmost column
a translation
- The delimiter | denotes that the matrix is composed of two submatrices.
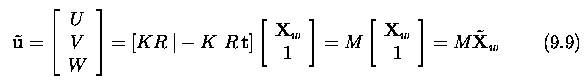
where ~X is the 3D scene point in homogeneous co-ordinates.
- The matrix M is called the projective matrix (also camera
matrix).
- It can be seen that the camera performs a linear projective transformation
from the 3D projective space P^3 to the 2D projective plane P^2.
- Introduction of projective space and homogeneous co-ordinates made
the expressions simpler.
- Instead of the nonlinear equation (9.4), we obtained the linear equation
(9.9).
- The 3x3 submatrix of the projective matrix M consisting of three leftmost
columns is regular, i.e. its determinant is non-zero.
- The scene point ~X_w is expressed up to scale in homogeneous co-ordinates
(recall that projection is expressed in the projection space) and thus
all alpha, M are equivalent for alpha not equal to 0.
- Sometimes the simplest form of the projection matrix M is used.
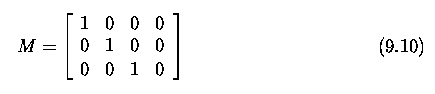
- This special matrix corresponds to the normalized camera co-ordinate
system, in which the specific parameters of the camera can be ignored.
- This is useful when the properties of stereo and motion are to be explained
in a simple way and independently of the specific camera.
An overview of single camera
calibration
- The calibration of one camera is a procedure that allows us to set
numeric values in the camera calibration matrix K (equation 9.6) or the
projective matrix M (equation 9.9).
- I. Intrinsic camera parameters only
- If the camera is calibrated, and a point in the image is known, the
corresponding line (ray) in camera-centered space is uniquely determined.
- II. Intrinsic and extrinsic parameters.
- Basic approaches to the calibration of a single camera.
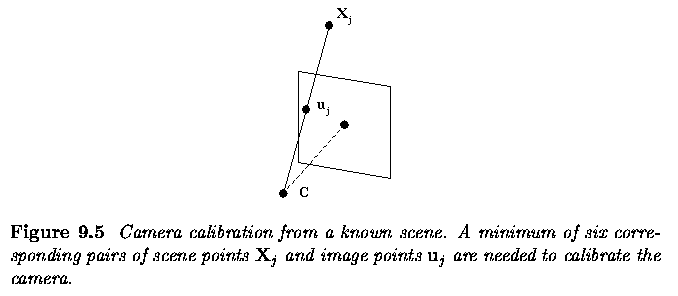
- A set of n non-degenerate (not co-planar) points lies in the 3D world,
and the corresponding 2D image points are known.
- Each correspondence between a 3D scene and 2D image point provides
one equation

- The solution solves an over-determined system of linear equations.
- The main disadvantage is that the scene must be known, for which special
calibration objects are often used.
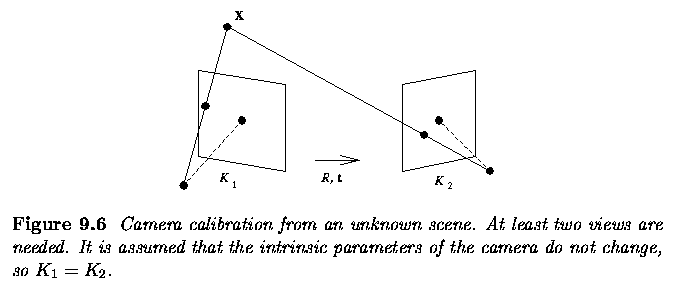
- More views of the scene are needed to calibrate the camera.
- The intrinsic camera parameters will not change for different views,
and the correspondence between image points in different views must be
established.
- A. Known camera motion:
- Both rotation and translation known:
- This general case of arbitrary known motion from one view to another
has been solved.
- Pure rotation:
- If camera motion is restricted to pure rotation, the solution can be
found.
- Pure translation:
- The linear solution (pure translation) can be found.
- B. Unknown camera motion:
- No a priori knowledge about motion, sometimes called camera selfcalibration.
- At least three views are needed and the solution is nonlinear.
- Calibration from an unknown scene is still considered numerically hard,
and will not be considered here.
Calibration of one camera
from the known scene
- Typically a two stage process.
- 1. The projection matrix M is estimated from the co-ordinates of points
with known scene positions.
- 2. The extrinsic and intrinsic parameters are estimated from M.
- (The second step is not always needed -- the case of stereo vision
is an example.)
- To obtain M, observe that each known scene point X=[x,y,z]^T and its
corresponding 2D image point [u,v]^T give one equation (9.11) - we seek
the numerical values m_ij in the 3x4 projection matrix M.
- Expanding from Equation (9.11)
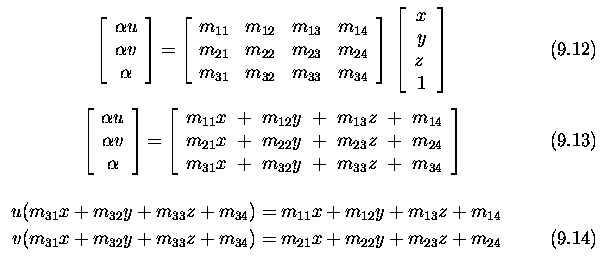
- Thus we obtain two linear equations, each in 12 unknowns m_11, ...
, m_34, for each known corresponding scene and image point.
- If n such points are available, we can write the equations 9.14 as
a 2n x 12 matrix
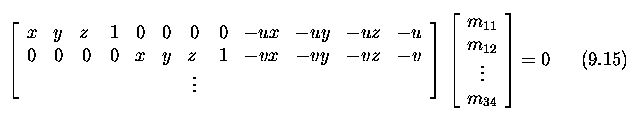
- The matrix M actually has only 11 unknown parameters due to the unknown
scaling factor, since homogeneous co-ordinates were used.
- To generate a solution, at least six known corresponding scene and
image points are required.
- Typically, more points are used and the over-determined equation (9.15)
is solved using a robust least squares method to correct for noise in measurements.
- The result of the calculation is the projective matrix M.
- To separate the extrinsic parameters (the rotation R and translation
t) from the estimated projection matrix M, recall that the projection matrix
can be written as
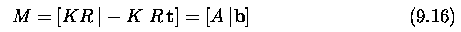
- Determining the translation vector is easy; we substituted A = K R
in equation (9.16), and so can write t = -A^-1 b.
- To determine R, note that the calibration matrix is upper triangular
and the rotation matrix is orthogonal.
- The matrix factorization method called QR decomposition will decompose
A into a product of two such matrices, and hence recover K and R.
- So far, we have assumed that the lens performs ideal central projection
as the pinhole camera does.
- This is not the case with the real lenses.
- Such a typical lens performs distortion of several pixels.
- A human observer does not notice it if he looks at general scene.
- In the case an image is used for measurements, the distortion from
the idealized pinhole model should be compensated.
- When calibrating a real camera, the more realistic model of
the lens includes two distortion components.
- First, the radial distortion bends the ray more or less than
in the ideal case.
- Second, the decentering displaces the principal point from the
optical axis.
- Recall that the five intrinsic camera parameters were introduced in
equation (9.8).
- Here, the focal length f of the lens is replaced by a parameter called
the camera constant.
- Ideally, the focal length and the camera constant should be the same.
- In reality, this is true when the lens is focused at infinity. Otherwise,
the camera constant is slightly less than the focal length.
- Similarly, the coordinates of the principal point can slightly change
from the ideal intersection of the optical axis with the image plane.
- The main trick of the intrinsic parameters calibration is to observe
a known calibration image with some regular pattern, e.g. blobs or lines
covering the whole image.
- The observed distortions of the pattern allows to estimate the intrinsic
camera parameters.
- Both the radial distortion and the decentering can be treated in most
cases as rotationally symmetric.
- They are often modeled as polynomials.
- Let u, v denote the correct image coordinates; ~u, ~v denote the measured
incorrected image coordinates that come from the actual pixel coordinates
x, y and the estimate of the position of the principal point ^u_0, ^v_0.

- The correct image coordinates u, v are obtained if the compensations
for errors delta u, delta v are added to the measured uncorrected image
coordinates ~u, ~v.

- The compensations for errors are often modeled as polynomials in even
powers to secure the rotational symmetry property.
- Typically elements up to maximally degree six are considered.
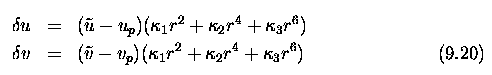
where u_p, v_p is the correction to the position of the principal
point.
- The r^2 is the square of the radial distance from the centre of the
image.
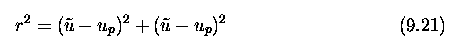
- Recall that ^u_0, ^v_0 were used in equation (9.18).
- The u_p, v_p are corrections to ^u_0, ^v_0 that can be applied after
calibration to get the proper position of the principal point.

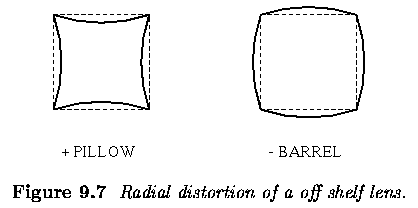
- Let's visualize typical radial distrortion of the lens for the simple
second order model as a special case of equation (9.20), i.e. no decentering
is assumed and second order polynomial approximation is considered
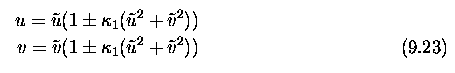
- The original image was a square pattern.
- The distorted images are shown

- The left part of the figure shows the pillow like distortion (minus
sign in equation (9.23), whereas the right part depicts the barrel like
distortion corresponding to the plus sign.
- There are more complicated lens models that cover tangential distortions
that model such effects as lens decentering.
Two cameras, stereopsis
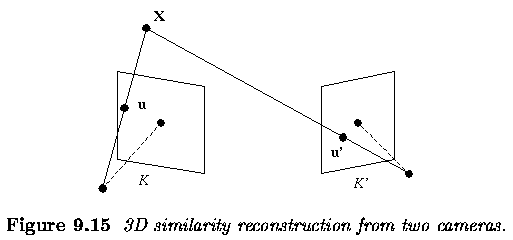
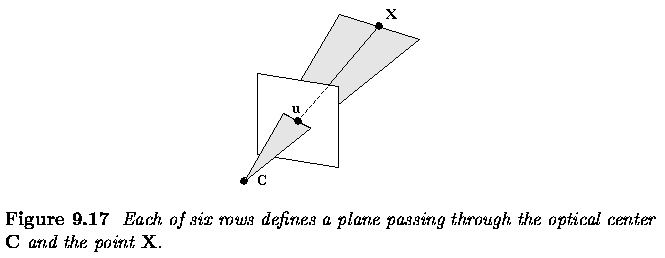
- Calibration of one camera and knowledge of the co-ordinates of one
image point allows us to determine a ray in space uniquely.
- If two calibrated cameras observe the same scene point X, its 3D co-ordinates
can be computed as the intersection of two such rays.
- This is the basic principle of stereo vision that typically
consists of three steps:
- Camera calibration;
- Establishing point correspondences between pairs of points from the
left and the right images
- Reconstruction of 3D co-ordinates of the points in the scene.
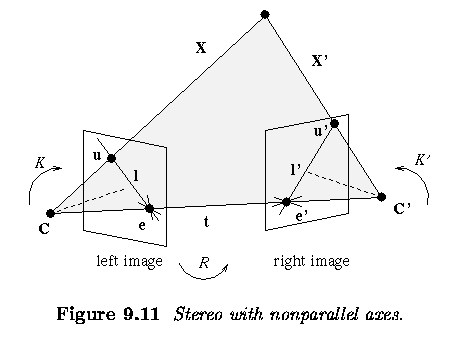
- The geometry of the system with two cameras

- The line connecting optical centers C and C' is called the baseline.
- Any scene point X observed by the two cameras and the two corresponding
rays from optical centers C, C' define an epipolar plane.
- This plane intersects the image planes in the epipolar lines
l, l'.
- When the scene point X moves in space, all epipolar lines pass through
epipoles e, e' - the epipoles are the intersections of the baseline
with the respective image planes.
- Let u, u' be projections of the scene point X in the left and right
images respectively.
- The ray CX represents all possible projections of the point X to the
left image, and is also projected into the epipolar line l' in the right
image.
- The point u' in the right image that corresponds to the projected point
u in the left image must thus lie on the epipolar line l' in the right
image.
- This geometry provides a strong epipolar constraint that reduces
the dimensionality of the search space for a correspondence between u and
u' in the right image from 2D to 1D.
- A special arrangement of the stereo camera, called the canonical configuration
is often used.
- The baseline is aligned to the horizontal co-ordinate axis, the optical
axes of the cameras are parallel, the epipoles move to infinity, and the
epipolar lines in the image planes are parallel.
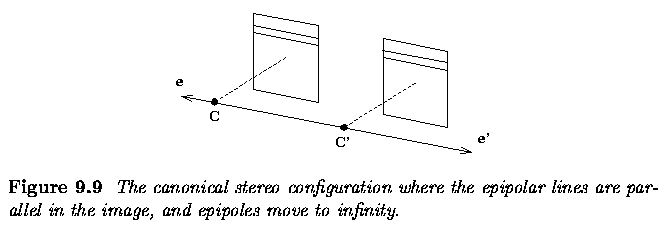
- For this configuration, the computation is slightly simpler.
- It is easier to move along horizontal lines than along general lines.
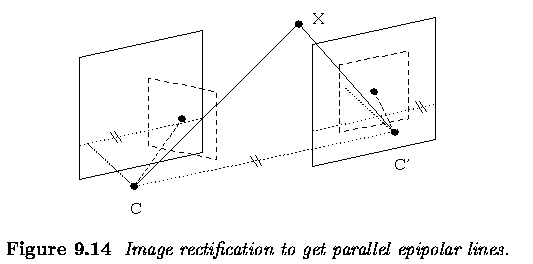
- The geometric transformation that changes a general camera configuration
with nonparallel epipolar lines to the canonical one is called image rectification.
- There are practical problems with the canonical stereo configuration,
which adds unnecessary technical constraints to the vision hardware.
- If high precision of reconstruction is an issue, it is better to use
general stereo geometry since rectification induces resampling that causes
loss of resolution.
- Let's consider an easy canonical configuration and recover depth.
- The optical axes are parallel, which leads to the notion of disparity
that is often used in stereo literature.
- In Figure, we have a bird's eye view of two cameras with parallel optical
axes separated by a distance 2 h.
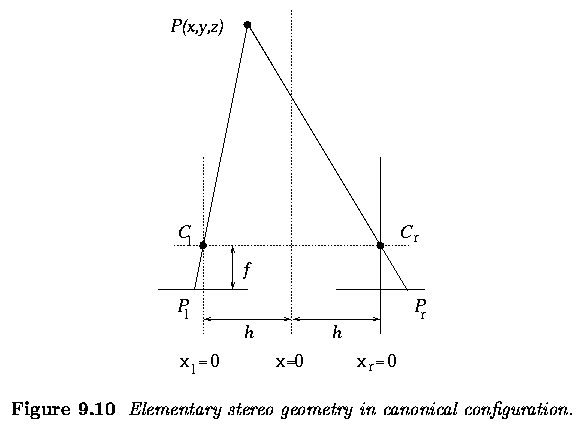
- The images they provide, together with one point P with co-ordinates
(x,y,z) in the scene, showing this point's projection onto left (P_l) and
right (P_r) images.
- The co-ordinates have the z axis representing distance from the cameras
(at which z=0) and the x axis representing horizontal distance (the y co-ordinate,
into the page, does not therefore appear).
- x=0 will be the position midway between the cameras; each image will
have a local co-ordinate system (x_l on the left, x_r on the right) which
for the sake of convenience we measure from the center of the respective
images; that is, a simple translation from the global x co-ordinate.
- P_l will be used simultaneously to represent the position of the projection
of P onto the left image, and its x_l co-ordinate - its distance from the
center of the left image (and similarly for P_r).
- It is clear that there is a disparity between x_l and x_r as a result
of the different camera positions (that is, | P_l - P_r | > 0); we can
use elementary geometry to deduce the z co-ordinate of P.
- P_l, C_l and C_l, P are the hypotenuses of similar right-angled triangles.
- h and f are (positive) numbers, z is a positive co-ordinate and x,
P_l, P_r are co-ordinates that may be positive or negative, we can then
write:

- and similarly from the right hand side of Figure 9.10

- Eliminating x from these equations gives


- Notice in this equation that P_r - P_l is the detected disparity
in the observations of P.
- If P_r-P_l = 0 then z = \infty.
- Zero disparity indicates the point is (effectively) at an infinite
distance from the viewer.
The geometry of two
cameras. The fundamental matrix
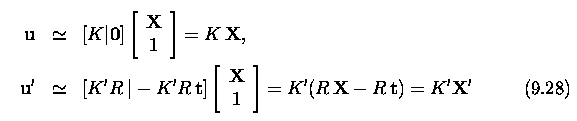

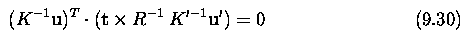
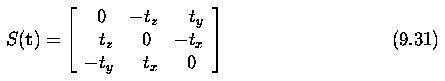

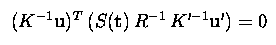
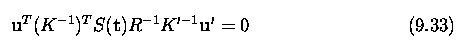
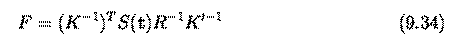

Relative motion of the
camera; the essential matrix
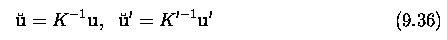




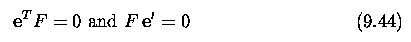
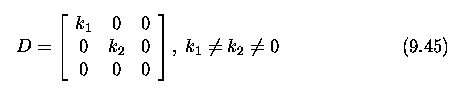
Estimation of a
fundamental matrix from image point correspondences

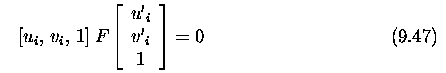
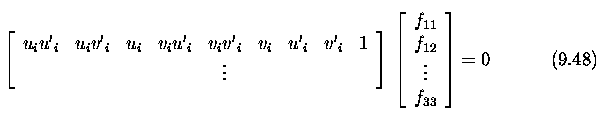


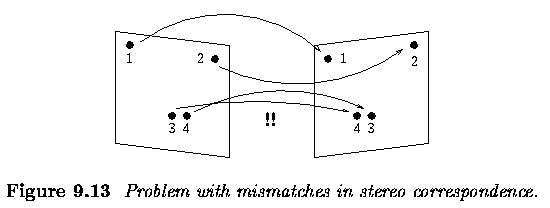
Applications of the epipolar
geometry in vision
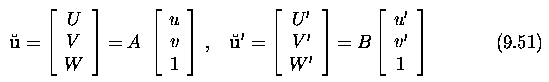
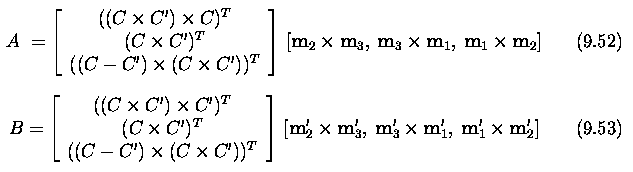

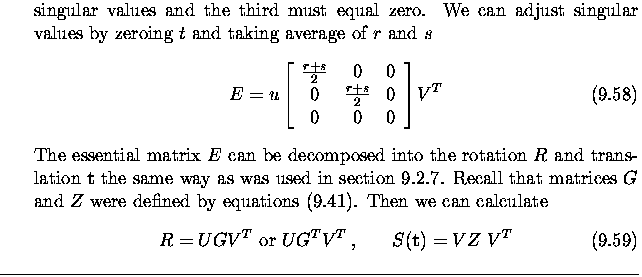
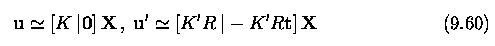

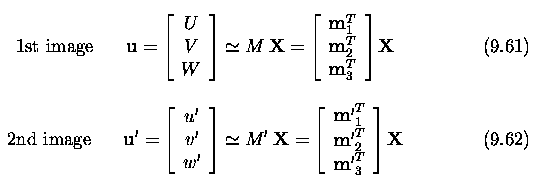
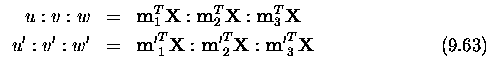
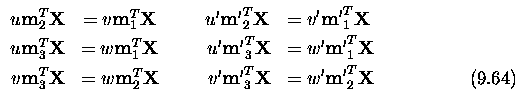
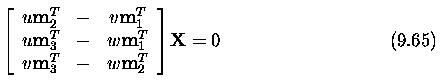
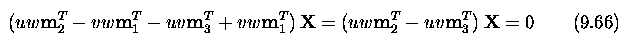

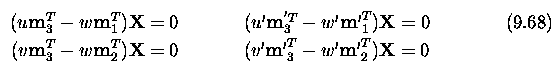
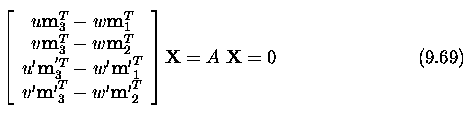

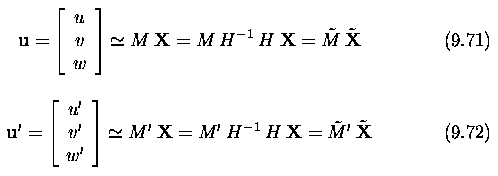
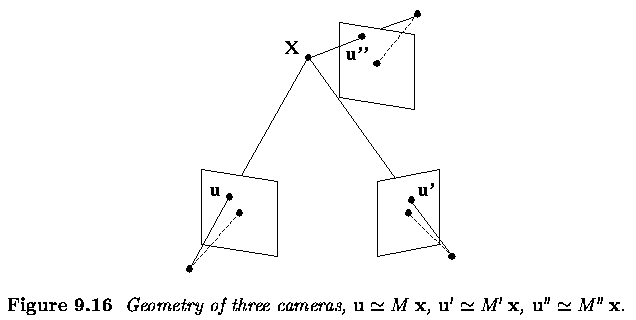
Three and more cameras
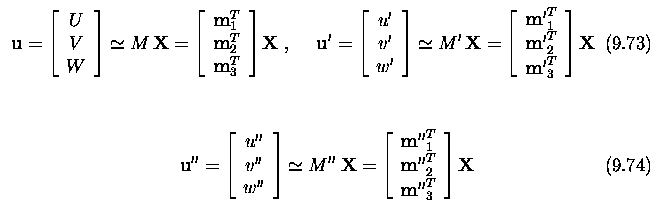
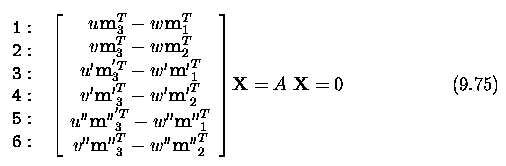
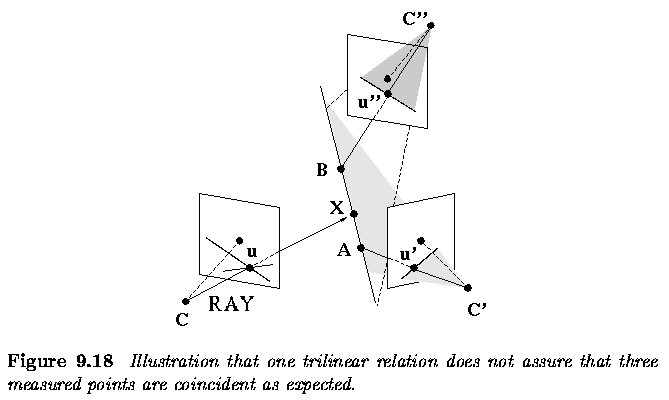
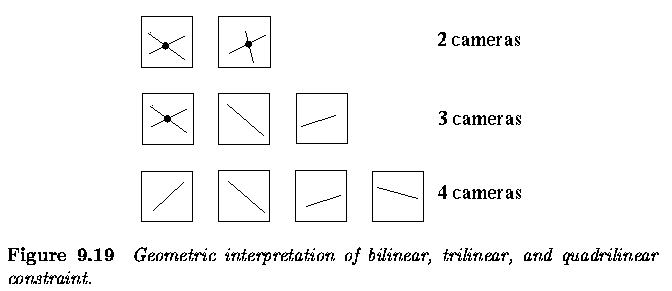

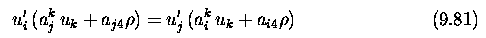
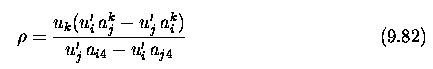
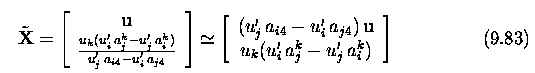

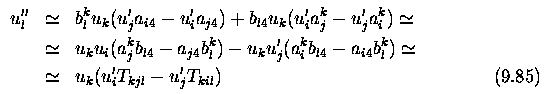
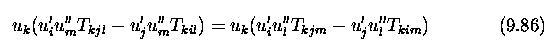
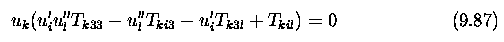
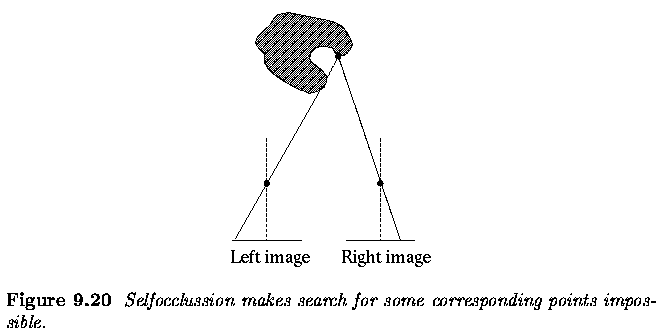
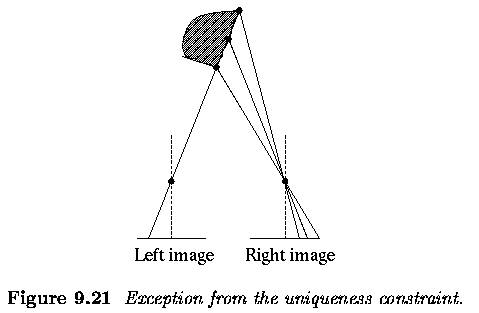
Stereo correspondence
algorithms
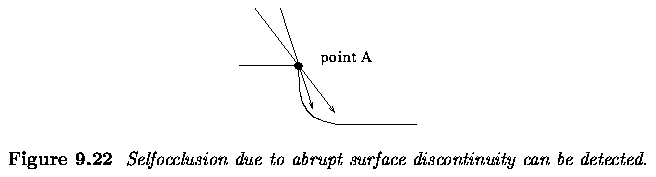
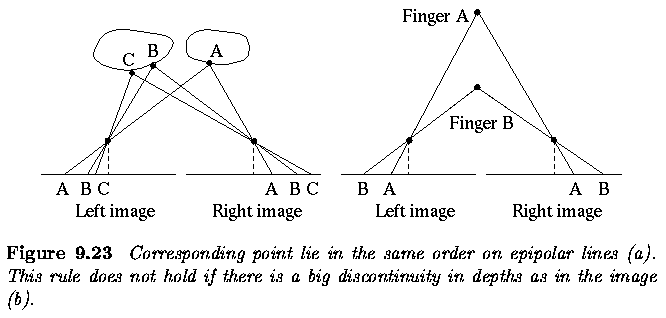
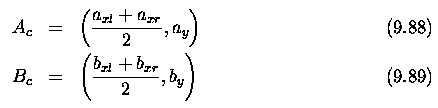
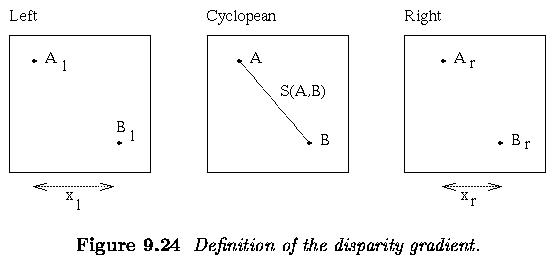
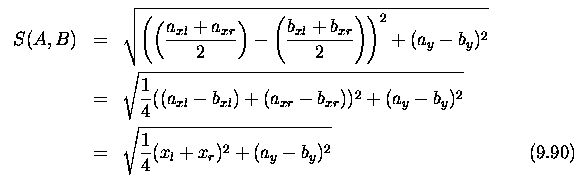
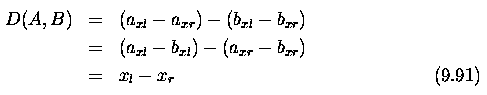
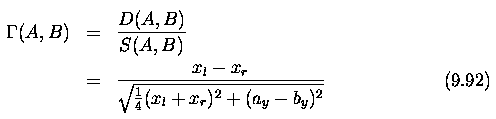

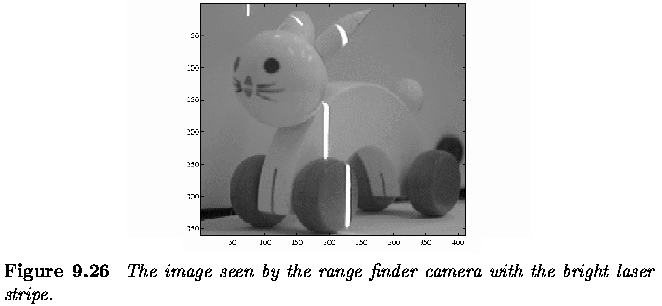
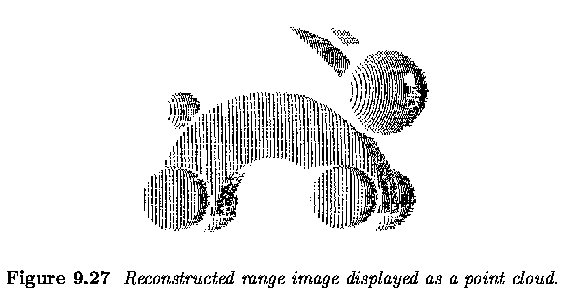
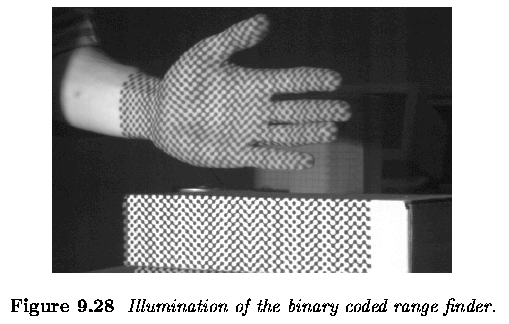
Active acquisition of range images
Last Modified: April 21, 1997
![[Go Back]](../IMAGES/next.gif)


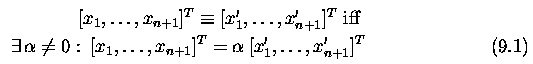
![]()

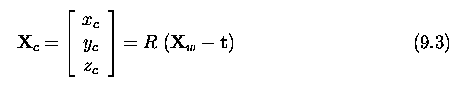
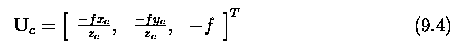

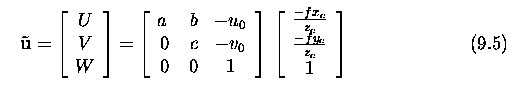
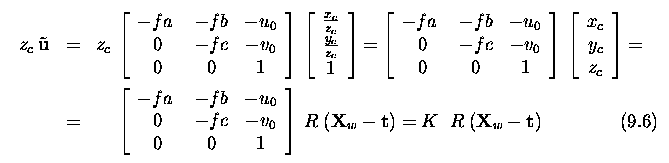
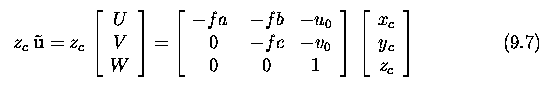
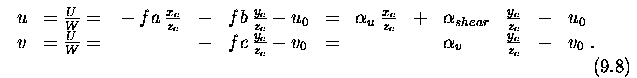
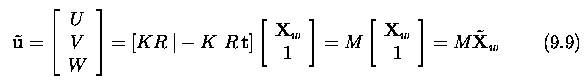
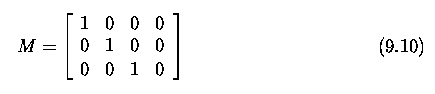



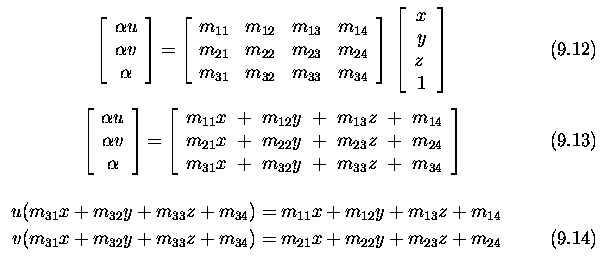
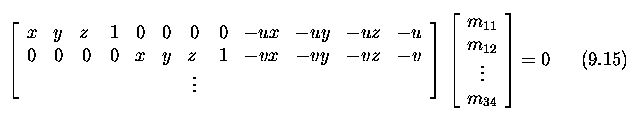
![]()



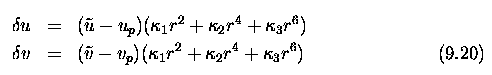
![]()

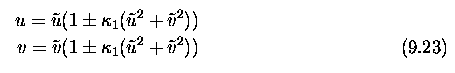









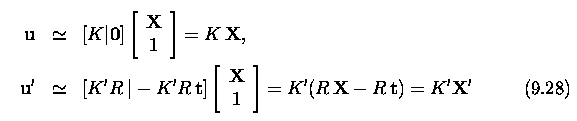
![]()
![]()
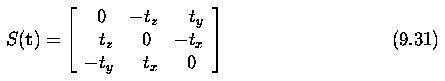
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
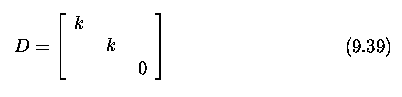
![]()
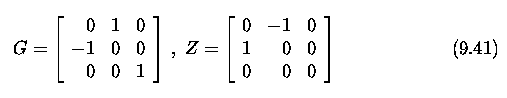
![]()
![]()

![]()
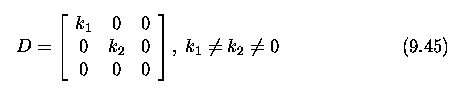

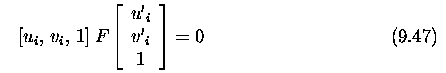
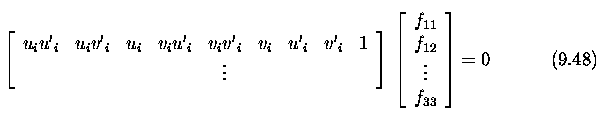
![]()



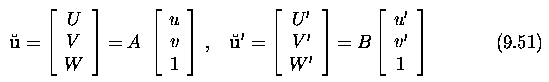


![]()

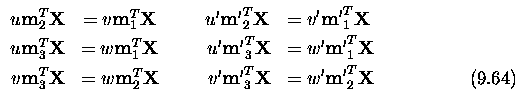
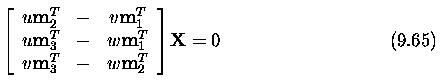
![]()
![]()
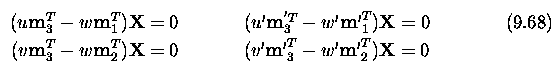
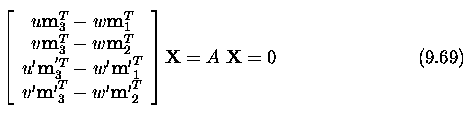
![]()
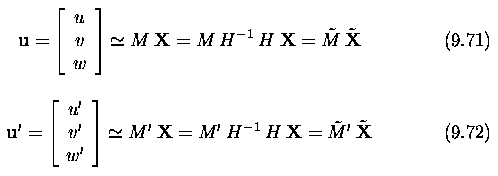

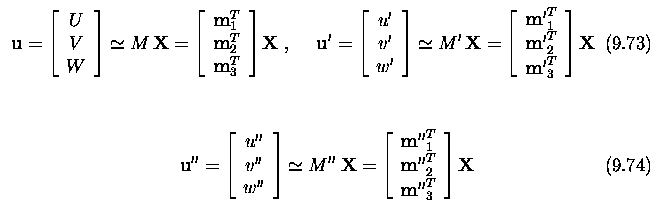
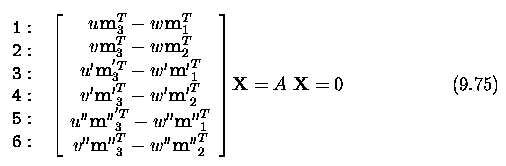




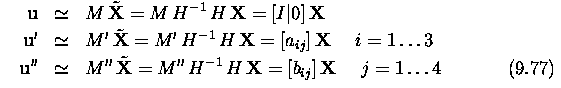

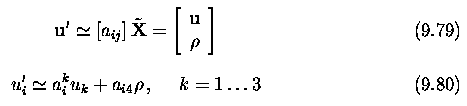
![]()
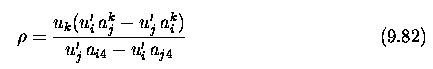
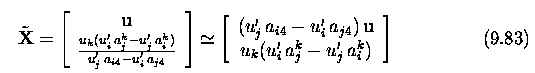
![]()
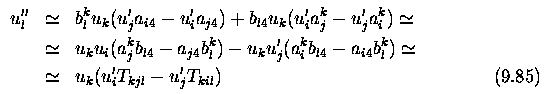
![]()